https://www.sfamgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/eco-friendly-packaging-for-medicines-in-glass.jpg
654
1154
SFAM
https://www.sfamgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/logo-sfam.svg
SFAM2025-09-11 17:19:452025-09-11 17:19:45Eco-design and sustainability in pharmaceutical packaging: the role of glass
https://www.sfamgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/eco-friendly-packaging-for-medicines-in-glass.jpg
654
1154
SFAM
https://www.sfamgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/logo-sfam.svg
SFAM2025-09-11 17:19:452025-09-11 17:19:45Eco-design and sustainability in pharmaceutical packaging: the role of glassGMP – Guide to Good Manufacturing Practices for Pharmaceuticals
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) are a regulatory framework essential to the pharmaceutical industry. GMP practices ensure the quality, safety, and efficacy of products.
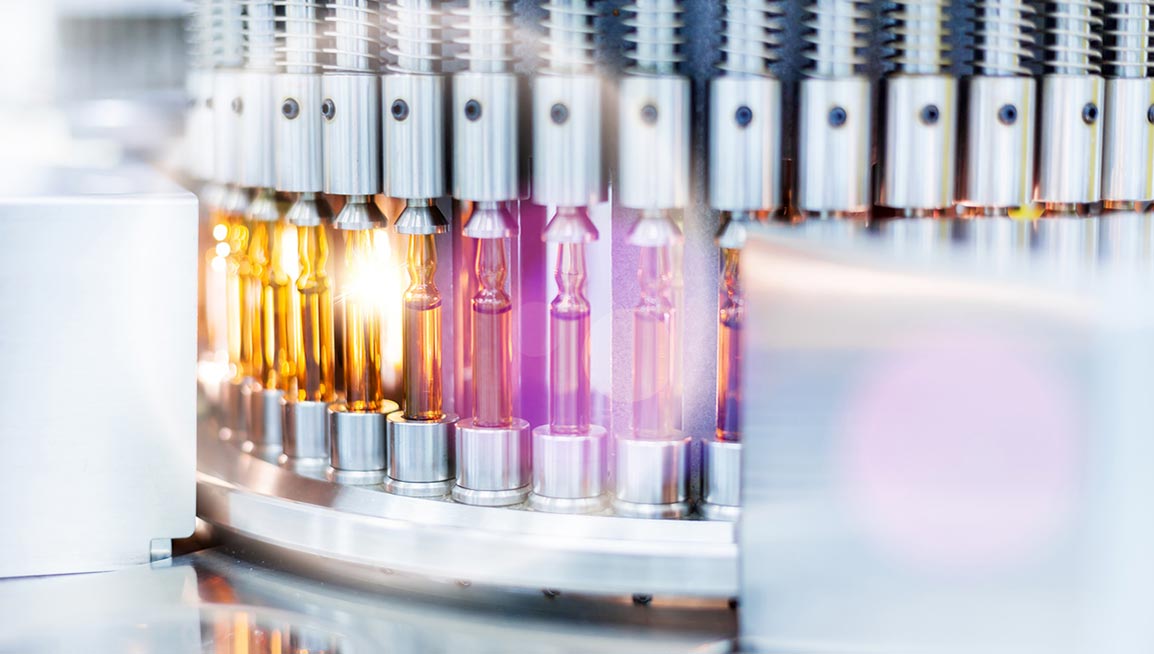

Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) are a regulatory framework essential to the pharmaceutical industry. GMP practices ensure the quality, safety, and efficacy of products.
In this article, we shall explain what GMPs’ are: their objectives, principles, and areas of application.
1. Definition of Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)
GMP are a set of guidelines and regulations formalized into processes and procedures, ensuring that industrial products (food, drugs, cosmetics, dietary supplements) are manufactured and controlled in compliance with quality standards, pharmaceutical GMP standards, applicable in the relevant territory.
Good Manufacturing Practices are issued by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a framework of regulations for industrial manufacturers, covering all aspects of production, from raw material management to the distribution of finished products.
By applying these practices, pharmaceutical manufacturers protect themselves and consumers by offering products with controlled quality.
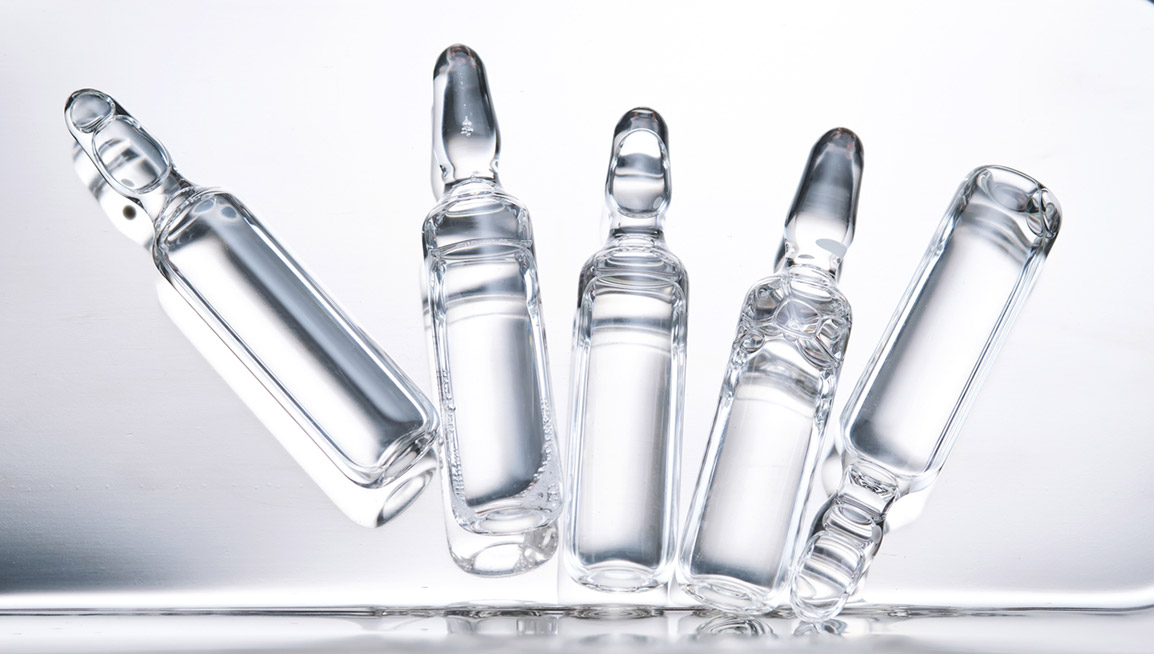
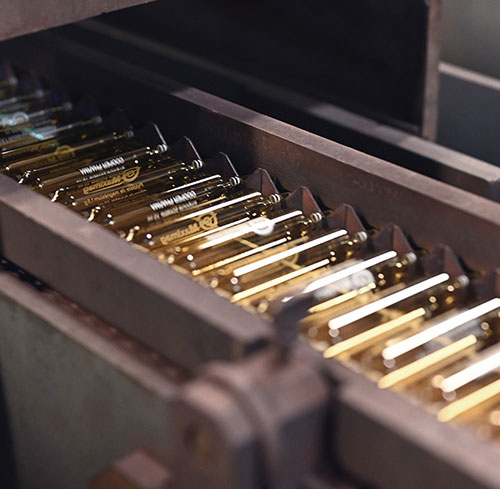
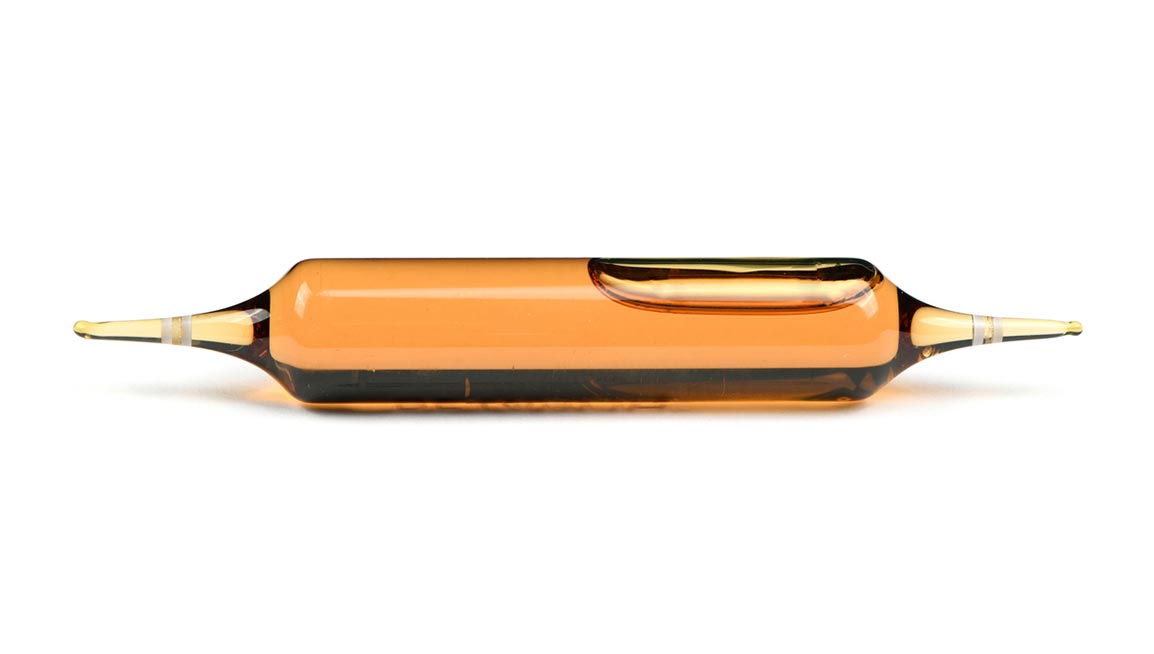
At SFAM, our double-tip glass ampoules are designed to meet the pharmaceutical GMP standards, governing pharmaceutical manufacturing and the production of dietary supplements as outlined by GMP. Discover the manufacturing of our double-tip ampoules, here.
2. The objectives of Good Manufacturing Practices for pharmaceuticals
GMP defines a regulatory framework that involves industrial manufacturers, such as those in the pharmaceutical industry, in a proactive approach to compliance and continuous improvement.
Good manufacturing practices (GMP) have 5 main objectives:
- Ensure product safety for consumers.
- Guarantee consistent quality.
- Prevent contamination and manufacturing errors.
- Provide complete product traceability.
- Facilitate regulatory compliance and reduce the risk of reminders and sanctions.
3. Pharmaceutical principles and GMP standards
GMPs’, including those for the pharmaceutical industry, are based on several principles:
- GMP and quality control:
Thanks to GMP, the production process is interspersed with strict controls. By intervening at different stages, these quality controls ensure adherence to standards and guarantee compliance with specifications. - GMP and hygiene:
Good manufacturing practices formalize hygiene standards for personnel, premises, industrial facilities and equipment. - GMP and training:
Regularly raising awareness and training staff on GMP facilitates adherence to operations and procedures, as well as the continuous improvement of manufacturing processes. - GMP and documentation:
GMP formalizes all stages of industrial manufacturing through the issuance of documents ensuring the traceability of operations and GMP audits. All manufacturing activities are recorded in detail, from production batches to quality controls and corrective actions. The documentation allows tracing the history of each product batch. - GMP and validation:
Documented validation provides proof of the monitoring carried out on equipment, production tools, handling, processes and more. It also demonstrates that products resulting from GMP are compliant with specifications. The main confirmations concern the validation of processes, cleaning operations, computer systems, and analytical methods. - GMP and audits:
Regular and unannounced audits ensure compliance with GMP. By identifying non-conformities to procedures, the audits facilitate the rapid implementation of corrective actions.
4. The application areas of GMP in the pharmaceutical industry
GMPs apply to 5 areas related to the pharmaceutical industry, but also to manufacturers of food supplements:
- Individuals:
Employees are required to apply pharmaceutical GMP standards. To do so, they must be made aware of the importance of GMP, trained and qualified. - Products:
GMP requires that raw materials and finished products undergo rigorous quality control throughout the manufacturing process. Finished products must be tested before they are released onto the market. Stability, purity, storage, packaging integrity and transport are also challenged. - Process:
Production processes must be defined, validated, documented, communicated to all employees, and regularly monitored to assess conformity of execution. - Procedures:
Standard operating procedures (SOPs) must be formalized and followed over time. These procedures cover all stages of production, from equipment cleaning to the packaging of finished products. - Premises:
Premises must be clean, well-maintained, adapted to production needs, and designed to minimize the risk of contamination.
5. Examples of GMP application
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) are fundamental to guaranteeing quality and safety in the pharmaceutical, cosmetics and dietary supplements industries.
For example, in pharmaceutical drug manufacturing, GMP ensures that every stage of the process, from receipt of raw materials to primary and secondary packaging, complies with strict manufacturing and quality control standards.
The dietary supplements industry also uses GMPs to ensure that products are manufactured under appropriate sanitary conditions.
Overall, the rigorous implementation of Good Manufacturing Practices for pharmaceutical products helps prevent errors, ensures compliance with regulatory requirements, guarantees product quality, and helps reinforce consumer confidence in the safety and efficacy of the products they use.